The shift to value-based payments has put the burden of reducing healthcare delivery costs on payers, providers and medical device companies.
With the increasing adoption of remote care monitoring and the ability of care teams to intervene before a potential episode, the spread of Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare is persistent and continuing to grow at a rapid pace, providing a significant opportunity for healthcare organizations to reduce the cost of care.
By 2025, Intel predicts the global worth of IoT technology from healthcare devices will constitute $2.5 trillion, and by 2020, will add $285 billion of healthcare provider value to the global economy1. As medical devices, wearables, electronic health records (EHRs) and other health IT systems become more interoperable and connected, we will see a system-of-systems evolution that will enable a fully digitized and connected healthcare continuum.
A connected healthcare ecosystem will make it easy for patients to access and track their health information and allow for seamless communication with their providers. IoT will play a significant role in enabling doctors, for the first time, to monitor patients remotely and prevent episodes of care in a timely manner. Providers will be able to manage populations efficiently and reduce the cost of healthcare delivery, improving the quality of patient experience and optimizing health system performance.
Signs of early IoT adoption exist in healthcare today. Consider some of the below use cases to see how the industry is embracing it:
A leading cardiac rhythm management company is building a platform to ingest and analyze patient-generated cardiac data. The vast data will be used for real-time patient monitoring and will enable doctors to prevent episodes of care.
A leading renal care device manufacturer is enabling care teams to remotely monitor patients that carry out dialysis in the comfort of patients' homes.
A leading cancer treatment device company is increasing customer satisfaction by remotely monitoring IoT-enabled devices and by providing proactive support to their customers.
A leading device manufacturer is aiding providers in preventing hospital-acquired infections by creating a closed-loop feedback mechanism for sterilizations of surgical equipment.
The Challenges
While IoT will certainly be a vital force in improving the quality of healthcare, potential challenges must also be considered.
Wielding great power. IoT has undoubtedly started to change the fabric of healthcare delivery. It provides access to previously unavailable data and insights – but with great power comes great responsibility. As confidential patient data leaves the four walls of a hospital, it's up to technology and service providers to ensure strong data protection and privacy. Having a "Cloud First" approach is critical to the success of IoT. The industry is already witnessing cloud service providers such as Amazon and Microsoft entering into HIPAA Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) to ensure patient data protection and privacy. However, to truly ensure patient data in encrypted throughout the healthcare continuum, one must engage with niche consulting companies.
Making sense of the data. The healthcare industry faces an intimidating challenge – handling vast amounts data. As the delivery model shifts to patient-centric care, it will be critical to create a single source of truth to build meaningful and correct analytics. Big data technology allows for structured and unstructured data sets to be stored and parsed. This technology, when coupled with powerful analytics tools, will drive the evolution of analytics.
The need for interoperability. The adoption of analytics in healthcare relies on the ability of organizations to integrate data sources to leverage for smarter decision-making. As the number of medical-related IoT devices grows, the challenge lies in ensuring the data is read into big data platforms and is easily integrated into analytics solutions.
Slower adoption rate. The healthcare industry has historically been a slow and cautious adopter of technology. As a lack of standardization, security protocols and interoperability continue to pose a threat, CIOs will remain wary of IoT adoption. However, with some of the largest healthcare systems and device manufacturers leading the change, IoT will continue to observe wide adoption rates.
Figure 1: IoT Point of View
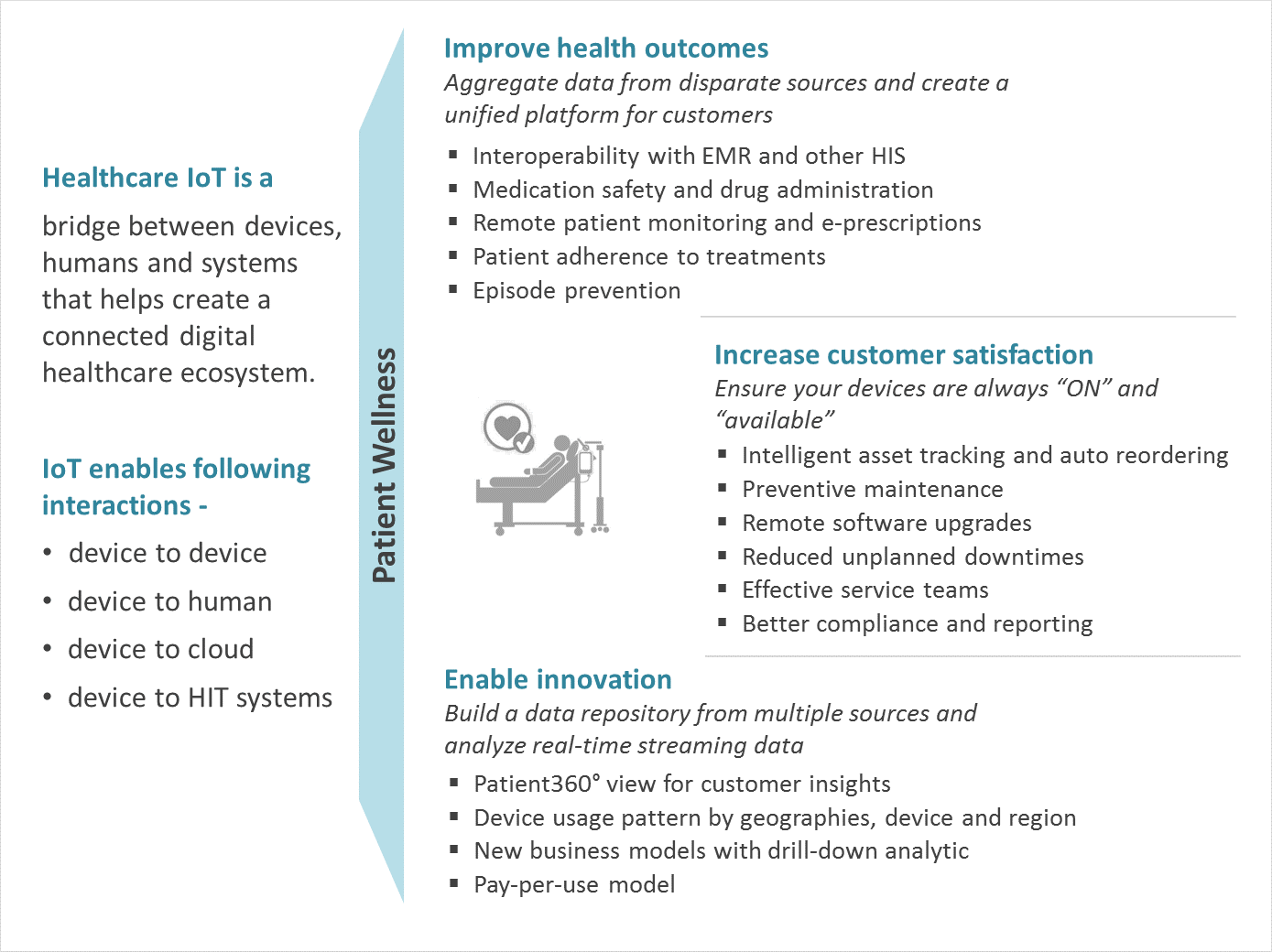
The time is now
We are only now seeing the tip of the IoT iceberg. With companies such as Apple and Google investing heavily in IoT, as well as the healthcare industry itself, we will see the emergence of new delivery models that are far more efficient and less costly. To stay ahead of the curve and NOT get disrupted, don't wait for standards to be set, but engage and track with standards and groups. In addition, don't fall prey to a "partial solution" trap; instead, look to build an ecosystem that supports your vision and platform. Engage with smaller and innovative startups – they sometimes have the best ideas. Finally, incorporate the IoT model into the core of your company. It will yield significant ROI and will help drive innovation dollars.
References:
1. http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/healthcare-it/solutions/documents/iot-healthcare-policy-principles-paper.html
The views, opinions and positions expressed within these guest posts are those of the author alone and do not represent those of Becker's Hospital Review/Becker's Healthcare. The accuracy, completeness and validity of any statements made within this article are not guaranteed. We accept no liability for any errors, omissions or representations. The copyright of this content belongs to the author and any liability with regards to infringement of intellectual property rights remains with them.

